Part One: Objectives
The mission of the programme is to cultivate students to be qualified civil engineers in Transport City Planning and Environmental Policy with appropriate theoretical knowledge, scientific thinking and problem-solving skills. Through this program, graduates will be educated comprehensively in ethics, intelligence, physical fitness and aesthetics, and oriented to fulfil the demand of building the 21th century modern global market-based-economy and the communism society. Graduates are also encouraged to possess firm lofty ambition, to be of noble personality and to be creative.
Though the cooperative education, domestic students will extend their background from both international culture and education aspects, to further advance the development of China’s economy and society, especially in the area of transportation engineering. The main teaching languages of this project are Chinese and English: the general education courses for Chinese are taught in Chinese, the disciplines and major related courses are taught in both Chinese and English, and the UCD courses are taught in English.
Part Two: Requirements
(1)Engineering knowledge: graduates will have solid mathematics, science fundamentals and transportation related knowledge including transportation planning, urban traffic management and control, and basic knowledge of transportation economics.
(2) Analysing problem: Graduates will be able to recognize, express and analyse complicated problems existing in transportation using principles and methods of mathematics, science and engineering, and can obtain substantive results.
(3) Design/develop solutions: graduates will be able to provide solutions to specific requirements of complicated engineering problems. They can take considerations of society, health, safety, legislation, culture and environment in designs for transportation production and operating system and put forward corresponding solutions to ensure the stable operation of system.
(4) Research: graduates will be able to conduct a preliminary research based on scientific principles and methods to solve related complicated engineering problems including experimental design, analysis and data processing, and reach a rational conclusion.
(5) Operation of modern tools: graduates can use traditional and web-based methods to search and collect informational and choose proper technologies, resources, and equipment to solve complicated engineering problems through simulation and prediction. Graduates can understand the limitation of technology used in their research.
(6) Engineering and society: graduates can evaluate the impact of engineering practice and project solutions to society, health, safety, legislation and culture based on rational analysis of project background and be aware of corresponding responsibilities.
(7) Environment and sustainability: graduates will understand and be able to evaluate the impact of complicated engineering practice to environment and sustainability of the society.
(8) Professional ethics: graduates will possess noble humanity, social responsibility, understand and follow engineering ethics in a project, and be willing to take corresponding responsibilities.
(9) Individual and groups: graduates will possess extended global vision, be able to accomplish jobs through team work under background of crossing disciplines and cultures.
(10) Live and learn: graduates will be aware of status and trends of modern technology, and be willing to make self-improvement through self-learning.
(11) Project management: graduates will understand principles of project management and financial tools and be able to manage a project under background of different disciplines and cultures.
(12) Communication: graduates will be fluent in both Chinese and English and will be able to communicate with international colleagues and the public on complex engineering projects.
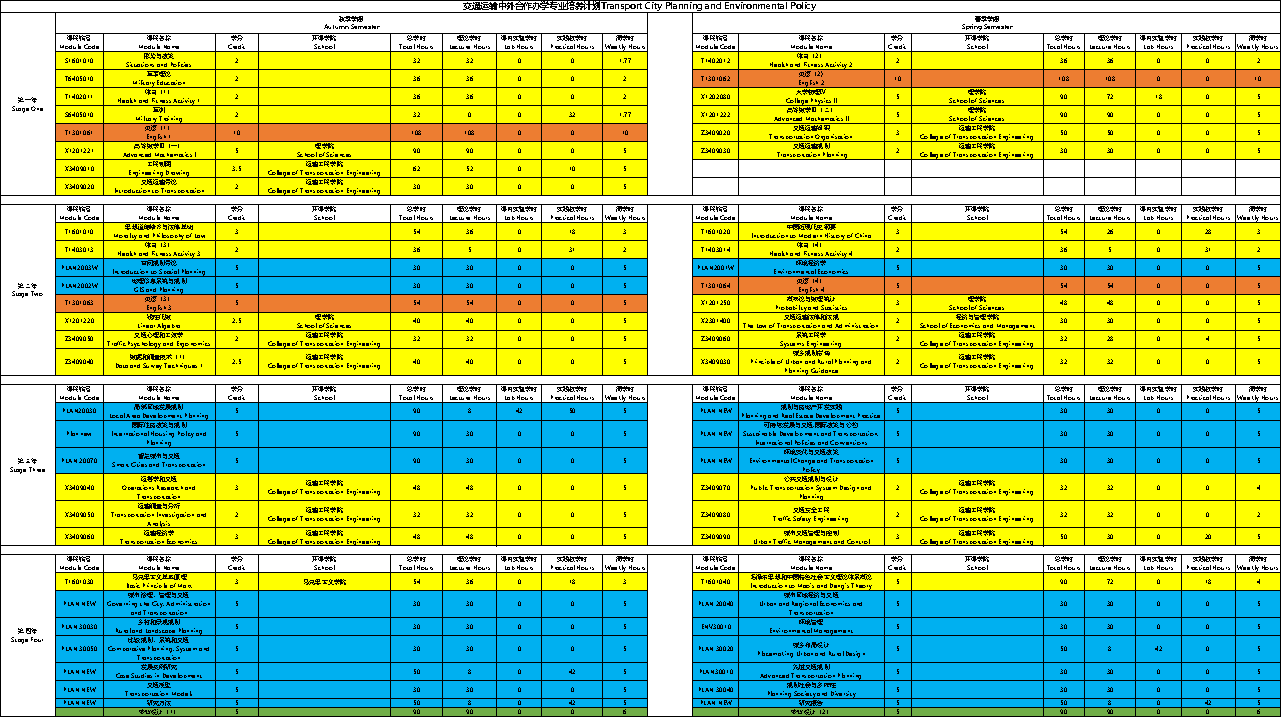
Part Three: Core courses
Chang’an University: Transportation Organization, Transportation Planning, Systems Engineering, Urban and Rural Planning Guidance, Transportation Investigation and Analysis, Transportation Economics, Traffic Safety Engineering, Urban Traffic Management and Control.
University College Dublin: Introduction to Spatial Planning, GIS and Planning, Environmental Economics, International Housing Policy and Planning, Local Area Development Planning, Smart Cities and Transportation, Planning and Real Estate Development Practice, Sustainable Development and Transportation: International Policies and Conventions, Environmental Change and Transportation Policy, Governing the City: Administration and Transportation, Rural and Landscape Planning, Comparative Planning: System and Transportation, Case Studies in Development, Transportation Models, Urban and Regional Economics and Transportation, Environmental Management, Placemaking of Urban and Rural Design, Advanced Transportation Planning, Planning Society and Diversity.
Textbooks &teaching materials of core courses, detailed description of the Practice Part and Engineering Report is attached.
According to programme objectives and industry demands, the curriculum is divided into General Education Courses, Discipline Basic Courses, Programme Basic Courses, Programme Optional Courses and Programme Public Optional Courses. Details refer to Table 1 and Table 2.
Part Four: Course Management
1. Establishment of special teaching management committee and teaching supervision group
A special teaching management committee is set up in this major, which is responsible for the examination and approval of the teaching plan, curriculum system, practical teaching system, curriculum syllabus, teaching methods and practice syllabus. The teaching management committee is mainly composed of the person in charge of professional construction and the director (deputy director) of the relevant teaching and research department.
At the same time, the teaching supervisory group is responsible for supervising the teaching of courses, practical teaching, graduation design, and curriculum design and so on. The supervisory group is mainly composed of senior professors.
The Teaching Management Committee and the Teaching Supervisory Group organize relevant work by holding meetings.
2. Establishment of Course Evaluation Mechanism
A special curriculum construction and evaluation committee has been set up in this major, which is responsible for the depth of curriculum syllabus, the examination and approval of the qualifications of lecturer, and the evaluation of teaching effect.
The evaluation is mainly based on on-site lectures, investigation reports, students' evaluation of teaching and peer evaluation.
3. Achievement evaluation method
Assessment results will be composed of examination results and homework results at the end of the course. The form of homework for different courses is different, which may include practice reports, quizzes, curriculum design and other forms. The grade in course assignments may include the homework completed online or on a computer. Some courses may include oral tests, extended reports/papers. Classroom assignments will receive timely feedback to help students learn repeatedly and gradually cultivate and strengthen their learning ability. Project evaluation also includes students' information retrieval skills, report writing skills and presentation skills.
4. Scholarship Settings
As with ordinary CHD students, they can apply for various scholarships of Chang'an University.
5. Student employment:
This students’ major employment orientations are: (1) overseas engineering work in domestic large-scale transportation enterprises. (2)engaged in the domestic government’s transportation departments or joint scientific research institutions related work. (3) further their master or PhD degree at home and abroad. (4) engaged in education, training and scientific research work in the fields of transportation engineering.
注: